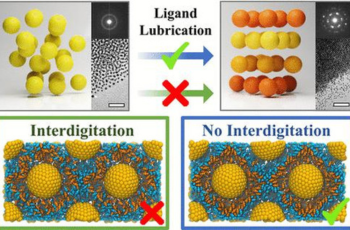
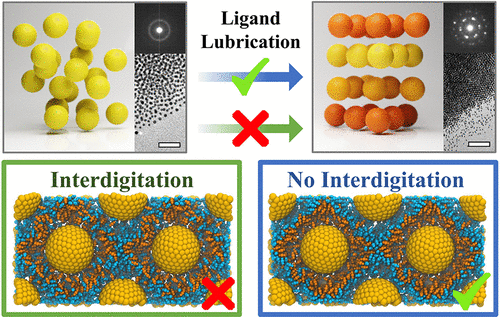
The size-dependent and collective physical properties of nanocrystals (NCs) and their self-assembled superlattices (SLs) enable the study of mesoscale phenomena and the design of metamaterials for a broad range of applications. However, the limited mobility of NC building blocks in dried NCSLs often hampers the potential for employing postdeposition methods to produce high-quality NCSLs. In this study, we present tailored promesogenic ligands that exhibit a lubricating property akin to thermotropic liquid crystals. The lubricating ability of ligands is thermally triggerable, allowing the dry solid NC aggregates deposited on the substrates with poor ordering to be transformed into NCSLs with high crystallinity and preferred orientations. The interplay between the dynamic behavior of NCSLs and the molecular structure of the ligands is elucidated through a comprehensive analysis of their lubricating efficacy using both experimental and simulation approaches. Coarse-grained molecular dynamic modeling suggests that a shielding layer from mesogens prevents the interdigitation of ligand tails, facilitating the sliding between outer shells and consequently enhancing the mobility of NC building blocks. The dynamic organization of NCSLs can also be triggered with high spatial resolution by laser illumination. The principles, kinetics, and utility of lubricating ligands could be generalized to unlock stimuli-responsive metamaterials from NCSLs and contribute to the fabrication of NCSLs.
Learn more about this work in the recent publications in Journal of the American Chemical Society.