Abstract
In this paper, we present an in-row and under-canopy autonomous navigation system for cornfields, called the Purdue Agricultural Navigation System or P-AgNav. Our navigation framework is primarily based on range view images from a 3D light detection and ranging (LiDAR) sensor. P-AgNav is designed for an autonomous robot to navigate in the corn rows with collision avoidance and to switch between rows without GNSS assistance or pre-defined waypoints. The system enables robots, which are intended to monitor crops or conduct physical sampling, to autonomously navigate multiple crop rows with minimal human intervention, thereby increasing crop management efficiency. The capabilities of P-AgNav have been validated through experiments in both simulation and real cornfield environments.
Published in: IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters ( Volume: 10, Issue: 4, April 2025)
https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10884071
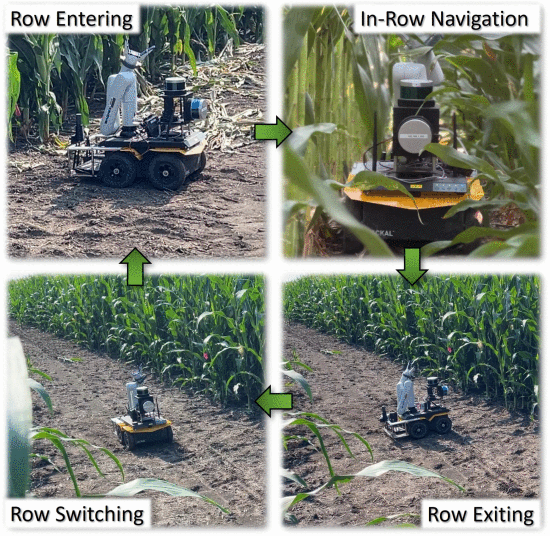
Figure: Our robot, P-AgBot, navigates under the canopies in multiple rows in real cornfields using the proposed P-AgNav in this work. P-AgNav is designed for autonomous multi-row crop monitoring and physical sampling in cornfields. P-AgNav handles all the necessary stages of navigation, which include row entering (top-left), in-row navigation (top-right), row exiting (bottom-right), and row switching (bottom-left), without relying on GNSS assistance or pre-defined waypoints.

